What you'll need to know...
KEY CONCEPT - Possibilities for managing resources sustainably and power over the decision-making process
Divergent thinking about population and resource consumption trends:
• pessimistic views, including neo-Malthusian views
• optimistic views, including Boserup
• balanced views, including resource stewardship
Resource stewardship strategies, including:
• the value of the circular economy as a systems approach for effective cycling of materials and energy
• the role of the UN Sustainable Development Goals and progress made toward meeting them
Synthesis, evaluation and skills opportunities
Different perspectives on global resource use and the likely effectiveness of management actions at varying scales
Divergent thinking about population and resource consumption trends:
• pessimistic views, including neo-Malthusian views
• optimistic views, including Boserup
• balanced views, including resource stewardship
Resource stewardship strategies, including:
• the value of the circular economy as a systems approach for effective cycling of materials and energy
• the role of the UN Sustainable Development Goals and progress made toward meeting them
Synthesis, evaluation and skills opportunities
Different perspectives on global resource use and the likely effectiveness of management actions at varying scales
Starter...
How can we feed a population of up to 11 billion people by the end of this century? Spend 23 minutes listening to the excellent BBC The Inquiry Podcast (click on image below), taking notes on the worksheet below as you go. Your notes should be around the four key witnesses and the impacts on securing food supplies for a growing global population (noting links to climate change).
Pessimistic V's Optimistic...
|
Task 1 - What does the term 'Malthusian' refer to?
Watch the first 4,40 minutes of the YouTube video to the right hand side and the slide 1-13 of the presentation (Credit Richard Allaway) below right and create an A4 fact sheet on Thomas Malthus using the note taking sheet above. Include facts, figures, projections & dates. Make sure you are clear on his views on the relationship between population size & resource consumption. This webpage is great too. Preventative checks: These are measures taken by humans to reduce shortages. This might be reducing population through better family planning and possibly anti-natalist policies. Or it could be reducing waste e.g. through better recycling. Positive checks: Despite their name, they are actually more negative solutions to resource shortages. These might be fighting and war or massive famines which actually reduce the overall population and therefore demand. Task 2 - Make a copy of the key terms above on your note taking sheet. Task 3 - What is neo-Malthusian? Neo-Malthusian: This is an idea of thought that follows Malthus's ideas. Paul Ehrlich and the ''Club of Rome" both have Neo-Malthusian ideas. Research and complete a fact file on Paul Ehrlich and the "Club of Rome". Use the note taking worksheet to do this. Your starting point is to study slide 8 on the PowerPoint from GATW. Again, make sure you are clear on their views of the relationship between population size and resource consumption today. Club of Rome & its Limits to Growth Model Study the 'Limits to Growth' model carefully.
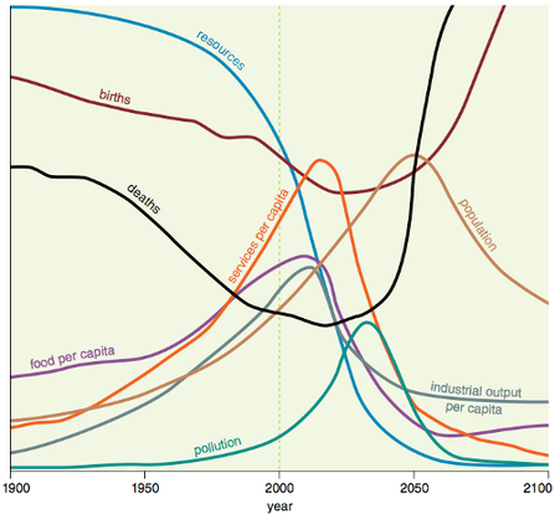
Task 4 - Take a copy of the graph (below right) and explain three of the relationships shown making reference to Nexus as well as climate change. |
|
What is Anti Malthusian?
Anti-Malthusian: Anti-Malthusian is simply the school of thought that disagrees with Malthus's pessimism and is more aligned to Boserup's optimism i.e. that humans will always find solutions to shortages.
Task 5 - Watch the three videos below and outline their key message as well as conflicts with the Malthusian message.
Task 6 - You are now going to create your fourth and final fact sheet for Ester Boserup. Use your note taking sheet from previous tasks. Remember, it is vital to highlight her views of the relationship between population size and resource consumption.
Anti-Malthusian: Anti-Malthusian is simply the school of thought that disagrees with Malthus's pessimism and is more aligned to Boserup's optimism i.e. that humans will always find solutions to shortages.
Task 5 - Watch the three videos below and outline their key message as well as conflicts with the Malthusian message.
Task 6 - You are now going to create your fourth and final fact sheet for Ester Boserup. Use your note taking sheet from previous tasks. Remember, it is vital to highlight her views of the relationship between population size and resource consumption.
|
|
|
|
Paper 2 Questions:
i. Outline the two opposing views of the relationship between population size and resource consumption.
ii. Analyse how the production of resources has kept up with rapid population increase.
i. Outline the two opposing views of the relationship between population size and resource consumption.
ii. Analyse how the production of resources has kept up with rapid population increase.
Resource Stewardship...
Lewis Carroll's Through the Looking Glass contains a famous passage describing Alice's attempts to run alongside the Red Queen in a topsy-turvy nonsense world, where cause and effect are reversed:
"Well, in our country," said Alice, still panting a little, "you'd generally get to somewhere else - if you run very fast for a long time, as we've been doing."
"A slow sort of country!" said the Queen. "Now, here, you see, it takes all the running you can do, to keep in the same place. If you want to get somewhere else, you must run at least twice as fast as that!"
The red queen's race seems an increasingly apt metaphor for environmental scarcity. Despite new discoveries, physical factors are making extraction costs higher and increasingly having an impact on local environments.
Source - The Guardian
|
Task 1 - Watch the video to the right hand side. Much of the content hints as to what the term 'Resource Stewardship' might refer to. Find your own definition of the term (making sure to include both the words 'social' and 'environmental' in there). Task 2 - Research what it meant by 'global commons' and why they are vulnerable in terms of resource consumption and security. Tragedy of the Commons In an obscure pamphlet in 1833, William Forster Lloyd described “a pasture open to all” supporting many herds, with natural forces keeping impacts “well below the carrying capacity of the land” – until the “day of reckoning” when: ... the rational herdsman [sic] concludes that the only sensible course for him to pursue is to add another animal to his herd. And another; and another ... But this is the conclusion reached by each and every rational herdsman sharing a commons. Therein is the tragedy. Each man is locked into a system that compels him to increase his herd without limit – in a world that is limited. Watch the second video to the right hand side. This explains the concept of the 'Tragedy of the Commons' and questions its application in modern society. Task 3 - Explain what tragedy of the commons refers to and find a recent news story (focusing on ineffective resource stewardship) that would highlight the issue. Task 4 - Watch the third and final video to the right and make notes on past governance of conservation issues; their limitations and how these approaches can be adapted to meet both social and environmental obligations. |
|
The value of the circular economy...
Recognising the interconnectedness of our world – the economy, society and the environment – lies at the heart of geography as a discipline. The circular economy applies systems thinking to resources, following flows of materials, energy and information, it also highlights the importance of seeing the bigger picture and understanding the world as a complex system, rather than one that is linear and predictable.
Introducing Dame Ellen MacArthur
Introducing Dame Ellen MacArthur
|
|
|
Task 1 - Watch the short summary video from Ellen MacArthur above.
Task 2 - Now watch the second video above, paying attention to the 'take, make, dispose' section and how we can move away from this.
Technical nutrients are strictly limited to non-toxic, non-harmful synthetic materials (plastics & metals) that have no negative effects on the natural environment (if they are not burnt or discarded); they can be used in continuous cycles as the same product without losing their integrity or quality. In this manner these materials can be used over and over again instead of being "downcycled" into lesser products, ultimately becoming waste.
Biological Nutrients are organic materials that, once used, can be disposed of in any natural environment and decompose into the soil, providing food for small life forms without affecting the natural environment. This is dependent on the ecology of the region; for example, organic material from one country or landmass may be harmful to the ecology of another country or landmass. Source.
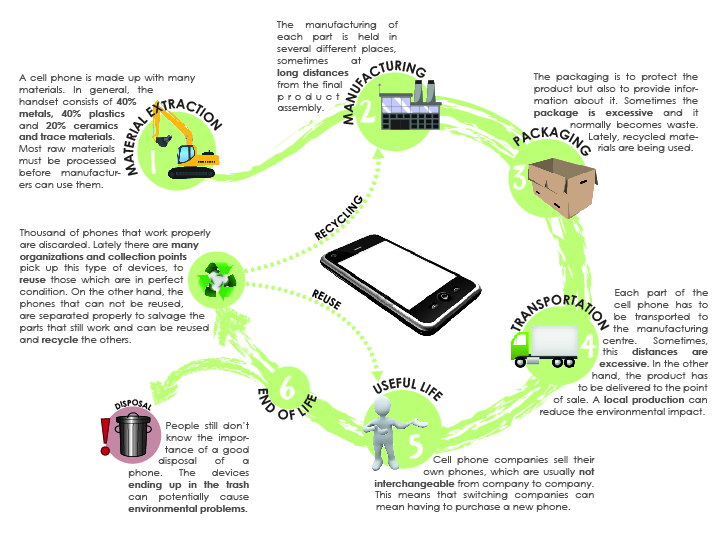
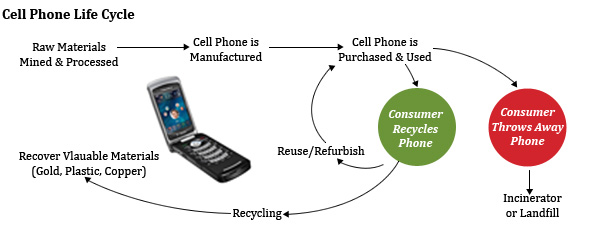
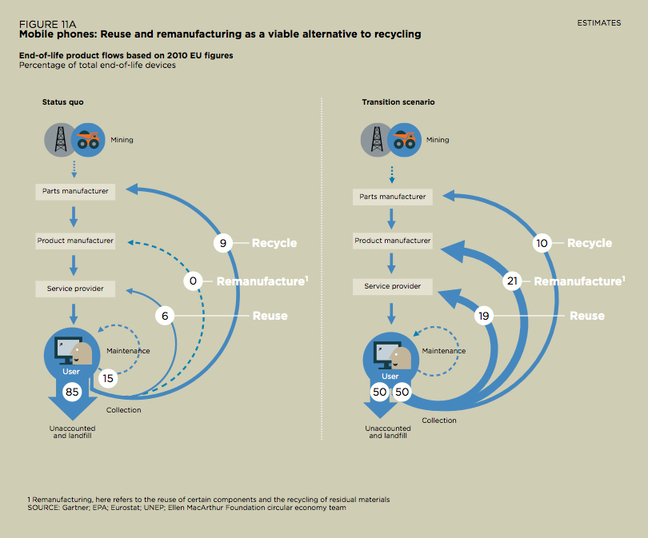
Case Study 1 - Mobile Phones
Task 3 - You are going to use your mobile phone as the focus for this piece of work. Watch the first video below for a brief mobile phone chemistry lesson! Using your notes so far and what you have seen today, complete the first page of the worksheet beneath as best as you can.
In the cradle to cradle model, all materials used in industrial or commercial processes—such as metals, fibers, dyes—fall into one of two categories: "technical" or "biological" nutrients. See this diagram.
Task 2 - Now watch the second video above, paying attention to the 'take, make, dispose' section and how we can move away from this.
Technical nutrients are strictly limited to non-toxic, non-harmful synthetic materials (plastics & metals) that have no negative effects on the natural environment (if they are not burnt or discarded); they can be used in continuous cycles as the same product without losing their integrity or quality. In this manner these materials can be used over and over again instead of being "downcycled" into lesser products, ultimately becoming waste.
Biological Nutrients are organic materials that, once used, can be disposed of in any natural environment and decompose into the soil, providing food for small life forms without affecting the natural environment. This is dependent on the ecology of the region; for example, organic material from one country or landmass may be harmful to the ecology of another country or landmass. Source.
Case Study 1 - Mobile Phones
Task 3 - You are going to use your mobile phone as the focus for this piece of work. Watch the first video below for a brief mobile phone chemistry lesson! Using your notes so far and what you have seen today, complete the first page of the worksheet beneath as best as you can.
In the cradle to cradle model, all materials used in industrial or commercial processes—such as metals, fibers, dyes—fall into one of two categories: "technical" or "biological" nutrients. See this diagram.
Task 4 - Now check out this page from Fairphone to see how they adopt a more circular approach to phone manufacture.
Check out this part of the Fairphone website and attempt to add some more detail (in different colour text to show differences between you phone & the fairphone) of the boxes on the second and third page of the work booklet with how Fairphone can use both biological & technical nutrient cycling with their products.
Task 5 - Conduct some research on a movement called 'Right to Repair' by using this page from Wired. Outline the campaign objectives and the barriers put in place by large e-manufacturers.
Task 6 - To what extent financially will it benefit TNC's such as Apple and Samsung to make their products 'last longer?'
|
|
|
Resources board - Mobile Phones - Linear to Circular
|
Case Study 2 - Children's Bikes Task 6 - Watch the introductory video to Islabikes taking notes as you go. Then read this Guardian article from 2016 to help to complete your own case study on the scheme. Why do children's bicycles have such short lifespans? Could this scheme be expanded to any other similar products? What are the limitations of such a scheme? The Bike Club Check out this example of a circular scheme like this in action. Spend a little time navigating through the pages to look at the selection of products available, the price (£) and the 'About Us' section. |
|
The role of the UN Sustainable Development Goals...
Update - April 2021
Check out the video below which reports on the recent pledge by countries to slash their emissions in the recent summit. The focus here is on the USA in 2021 and its pledge to reduce emissions by 50% - some say far more than they pledged in Paris 2015...
Then check out the second goal, a 2021 BBC News report from India about their increasing need for coal in the country's quest for further economic development. The peak demand for coal is not expected until the 2030's throwing in to doubt their ability to meet their 2030 goal commitments.
Check out the video below which reports on the recent pledge by countries to slash their emissions in the recent summit. The focus here is on the USA in 2021 and its pledge to reduce emissions by 50% - some say far more than they pledged in Paris 2015...
Then check out the second goal, a 2021 BBC News report from India about their increasing need for coal in the country's quest for further economic development. The peak demand for coal is not expected until the 2030's throwing in to doubt their ability to meet their 2030 goal commitments.
|
|
|
The content of this report will have clear implications on the ability to meet the following two goals and the fact that 2030 is being banded about is a clear reference to the end date of these goals.
For this task, we will be focusing on the following two Goals that lend themselves particularly well to wrapping up this whole unit of work on Global Resource Consumption & Security.
Task 1 - You are going to produce a presentation that will act as a 'progress check' on the spatial patterns of progress on each of the two goals above.
You can click on each logo to access the un.org page that gives full details on each of the goals, the sub goals, targets and progress reports.
You can click on the tabs above to be taken to a progress check from 2020 on each goal.
There should be a focus on the April 2021 summit where agreements were reached that will have overarching impacts on the two goals above. For a USA perspective, please read this White House press statement (22/04/2021), particularly the bottom 1/3 of the sheet.
Two of the presentations will be chosen to be presented 'live' in the classroom once the work has been submitted and checked by your teacher.
The Presentation (please do the following for both goals)
Process (Global Trends in Production)
Place (Impacts of Changing Trends)
Power & Possibility (Resource Stewardship)
Slide 1 - Logo & choose any two targets from the section entitled 'Goal 7 / 12 Targets'
Slide 2 - Explanation of the processes that have led to this target being implemented.
Slide 3 - Mapping (use this link) the global progress in attaining the goal and describe at least two places that have made / not made satisfactory progress with a brief explanation as to why.
Slide 4 - A brief update on the overall global progress made towards (possibility & power) meeting that goal.
You can click on each logo to access the un.org page that gives full details on each of the goals, the sub goals, targets and progress reports.
You can click on the tabs above to be taken to a progress check from 2020 on each goal.
There should be a focus on the April 2021 summit where agreements were reached that will have overarching impacts on the two goals above. For a USA perspective, please read this White House press statement (22/04/2021), particularly the bottom 1/3 of the sheet.
Two of the presentations will be chosen to be presented 'live' in the classroom once the work has been submitted and checked by your teacher.
The Presentation (please do the following for both goals)
Process (Global Trends in Production)
Place (Impacts of Changing Trends)
Power & Possibility (Resource Stewardship)
Slide 1 - Logo & choose any two targets from the section entitled 'Goal 7 / 12 Targets'
Slide 2 - Explanation of the processes that have led to this target being implemented.
Slide 3 - Mapping (use this link) the global progress in attaining the goal and describe at least two places that have made / not made satisfactory progress with a brief explanation as to why.
Slide 4 - A brief update on the overall global progress made towards (possibility & power) meeting that goal.