What you'll need to know...
KEY CONCEPT - How pressure on resources affects the future security of places
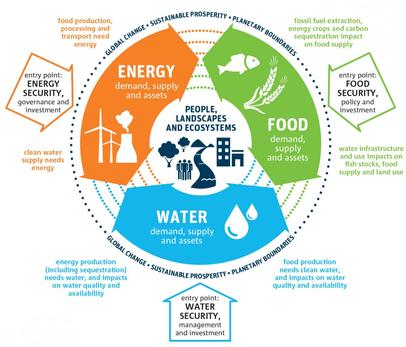
The water–food–energy “nexus” and how its complex interactions affect:
• national water security, including access to safe water
• national food security, including food availability
• national energy security, including energy pathways and geopolitical issues
The implications of global climate change for the water–food–energy nexus
• Detailed examples of two countries with contrasting levels of resource security
The disposal and recycling of consumer items, including international flows of waste
Synthesis, evaluation and skills opportunities
How perspectives on, and priorities for, national resource security vary between places and at different scales
The water–food–energy “nexus” and how its complex interactions affect:
• national water security, including access to safe water
• national food security, including food availability
• national energy security, including energy pathways and geopolitical issues
The implications of global climate change for the water–food–energy nexus
• Detailed examples of two countries with contrasting levels of resource security
The disposal and recycling of consumer items, including international flows of waste
Synthesis, evaluation and skills opportunities
How perspectives on, and priorities for, national resource security vary between places and at different scales
The Food - Water - Energy Nexus (FEW) ... What is it?

The video tutorial for this lesson is available here. A PDF version of the lesson plan is available from the IB DP Geography site or by clicking here.
"Trade-offs between energy and water, or between energy and food, are increasingly being debated in terms of the 'nexus' – a buzzword which has risen in prominence over the past few years as a way of thinking about interconnections between food, water, energy and the environment. These systems are inextricably linked, and integrated approaches are required, which move beyond sectoral, policy and disciplinary silos" - James Wilsdon and Rose Cairns June 2014
Task - We are going to use solo hexagons to critically examine the complexities between the Nexus of water, food, energy and climate change. To to this the following resources are important.
Step 1 - The Preparation
Split your teaching group into pairs or groups of three. Explain to the students that they are going to be completing a hexagon activity and that there is no right or wrong answer. The key thing is the discussion that goes with the activity and making as many links between as many global issues as possible.
Step 2 - The Traditional Approach
Step 3 - The Nexus Approach & Critical Thinking
Now distribute 'Hexagon Card Set 2' and now ask the students to complete their diagrams. This may involve completely starting over again with their hexagon structure in order to incorporate this new nexus approach. Note that some of these cards are specific to issues in the area surrounding the International School of Toulouse, but can be adapted to suit your school area.
Step 4 - The final display
Step 5 - Links with the SDG's
Step 6 - Exam Corner
“Water, food and energy security can no longer be viewed as isolated global problems” – critically examine this statement (10)
"Trade-offs between energy and water, or between energy and food, are increasingly being debated in terms of the 'nexus' – a buzzword which has risen in prominence over the past few years as a way of thinking about interconnections between food, water, energy and the environment. These systems are inextricably linked, and integrated approaches are required, which move beyond sectoral, policy and disciplinary silos" - James Wilsdon and Rose Cairns June 2014
Task - We are going to use solo hexagons to critically examine the complexities between the Nexus of water, food, energy and climate change. To to this the following resources are important.
Step 1 - The Preparation
- Ensure that students have a pair of scissors each, a glue stick and A2 sized sugar paper for the final display.
- Four sets of cards should be available to the students (see above card sets)
- An interactive whiteboard (useful but not essential)
Split your teaching group into pairs or groups of three. Explain to the students that they are going to be completing a hexagon activity and that there is no right or wrong answer. The key thing is the discussion that goes with the activity and making as many links between as many global issues as possible.
Step 2 - The Traditional Approach
- Distribute 'Hexagon Card Set 1' (above right) and ask students to sort out the statements first into groupings and then to start making links between the groups. Possible groupings:
- 1. What is nexus? 2. Past trends 3. Future trends (may include rise of the middle class otherwise this could be a category in its own right) 4. Climate change 5. Water 6. Food 7. Energy 8. Other info
- If you have an interactive whiteboard, you may want to click on the link to 'Set 1 - Interactive' and use this to ask the students to show their results visually at the end of this step.
- The students may add any additional hexagon cards by writing them on the blanks provided and adding to their diagram
- Prompt discussion about the 'traditional' viewpoint of these global issues and how these groups of issues that have been tackled independently. Do they simply have small sub-groups of hexagons separate from each other?
Step 3 - The Nexus Approach & Critical Thinking
Now distribute 'Hexagon Card Set 2' and now ask the students to complete their diagrams. This may involve completely starting over again with their hexagon structure in order to incorporate this new nexus approach. Note that some of these cards are specific to issues in the area surrounding the International School of Toulouse, but can be adapted to suit your school area.
- Students can be given a chance to add their own cards to the diagram and there should be plenty of discussion of how they have come to the formation on their display card.
- A possible ordering can be seen by clicking on the link for 'Set 2 - Interactive'
Step 4 - The final display
- The students would then be given time to organize their cards (paper versions) onto display card.
Step 5 - Links with the SDG's
- A plenary would include a final pack of hexagons each with the logo of the 17 SDG’s where students have to fit them into the diagram as extensions to the hubs and nodes that they already have glued down.
Step 6 - Exam Corner
- The sequence of the hexagons diagram could then be further examined by using a hexagons Venn Diagram and ultimately used in conjunction with the IB essay planner to formulate a response to the following Paper 2 - 10 mark homework question
“Water, food and energy security can no longer be viewed as isolated global problems” – critically examine this statement (10)
Your overall connecting examples are probably going to be the following:
1. Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam - link to a very good source of information (scroll down to 'Why GERD?'
2. Biofuels - link to an excellent source of information (focus on drawbacks & benefits).
1. Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam - link to a very good source of information (scroll down to 'Why GERD?'
2. Biofuels - link to an excellent source of information (focus on drawbacks & benefits).
|
|
|
Revision - The FEW Nexus in Summary...
You are going to be completing three brief summary sheets that show how the Nexus complex interactions affect:
• national water security, including access to safe water
• national food security, including food availability
• national energy security, including energy pathways and geopolitical issues
Your starting point is to read this summary article from United Nations Water - here.
Now spend 28 minutes listening to this excellent Podcast from the BBC Business team and take notes.
Split into groups of three. Each person in the group is focus on one of the areas below. Your job is to research your interactions and produce a presentation to give to your partner on the issue as well as a completed exam question (3+3) as follows:
1. Describe how Nexus interactions affect national water security and access to safe water.
2. Identify how Nexus interactions affect national food security and food availability.
3. Explain how Nexus interactions affect national energy security and geopolitical issues.
You must include one global 'case study' example in your presentation and exam response.
• national water security, including access to safe water
• national food security, including food availability
• national energy security, including energy pathways and geopolitical issues
Your starting point is to read this summary article from United Nations Water - here.
Now spend 28 minutes listening to this excellent Podcast from the BBC Business team and take notes.
Split into groups of three. Each person in the group is focus on one of the areas below. Your job is to research your interactions and produce a presentation to give to your partner on the issue as well as a completed exam question (3+3) as follows:
1. Describe how Nexus interactions affect national water security and access to safe water.
2. Identify how Nexus interactions affect national food security and food availability.
3. Explain how Nexus interactions affect national energy security and geopolitical issues.
You must include one global 'case study' example in your presentation and exam response.
For this task, you can visit the rather excellent geographyalltheway site (subscription required). Your case study will be a comparison of Switzerland and the United Arab Emirates and there contrasting levels of food, energy and water security. Click here to access the relevant page and use the worksheet beneath to record your information.
If you do not have access to geographyalltheway, you can use the hyperlinks that are provided on the worksheet to guide your data collection. Once your data and information gathering is complete, please write your response to the following exam question:
Compare and contrast the national resource security of two countries that you have studied [10 marks]
If you do not have access to geographyalltheway, you can use the hyperlinks that are provided on the worksheet to guide your data collection. Once your data and information gathering is complete, please write your response to the following exam question:
Compare and contrast the national resource security of two countries that you have studied [10 marks]
|
|
|
Impacts of Climate Change on the FEW Nexus...
This is an independent research task and would best suit a homework type approach. Download and print out the sheet below in A3 size and use the information contained within the WWF Fact Sheet to help you extract the key issues of the effects of Climate Change on the FEW Nexus.
The disposal and recycling of consumer items, including international flows of waste...
Part 1 - E-Waste
What do we own?
There is a very good chance that somewhere in your house, you have a drawer or a box that resembles the image below. Perhaps a quick show of hands to see who has one of these? Briefly discuss why we keep these items. Record your ideas on the worksheet above.
There is a very good chance that somewhere in your house, you have a drawer or a box that resembles the image below. Perhaps a quick show of hands to see who has one of these? Briefly discuss why we keep these items. Record your ideas on the worksheet above.
Why do we generate so much waste?
Watch the video below and fill in the activities on the worksheet, as indicated. You will be focusing on the so-called 'Designed for the dump' and 'Planned obsolescence' elements of the electronics.
So, in theory, TNC's like DELL are able to drastically reduce their impacts on the environment by recycling. Let's focus on the journey of electronic waste generated in the USA.
|
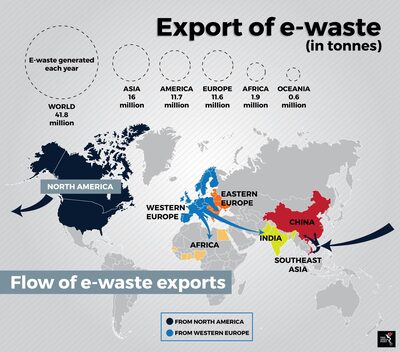
Where does the waste go when we have finished with it?
The image to the right is from the Basel Action Network, more about them later. On your worksheet, describe the major flows between places. You may well be accessing this work using a DELL computer. The company has gone from strength to strength over recent years and in 2019 shipped 260 million electronic units. But what happens when these products reach the end of their life cycle? Check out the video below to find out about the partnership between DELL and a company called Goodwill. |
Part 1 - USA to Asia
The first part of this study will focus on the transit of materials from the USA to Hong Kong, where some of the materials are processed before being sent onward. Watch the video below and complete the activities on the worksheet.
Here is the interactive map to show the movement of the items of e-waste as recorded by the tracker devices.
Part 2 - Europe to West Africa
200,000 tonnes of e-waste disposed of from HICs, often from Europe makes it way to the west of Africa and in particular to Ghana. Once it has been unloaded from the container ships, it is transported to the now infamous Accra suburb of Agbogbloshie. Take a trip up and down the road that leads past one of the biggest "decommissioning" sites in Agbogbloshie.
What evidence can you see of the transfer of international waste. Complete the activity on the worksheet.
|
|
|
Now, watch the drone footage of what the site looks like from the air. Follow this by watching the BBC News video above. Complete the activity in the space above.
Part 2 - Recycling
|
|
|
Task. Complete the note taking frame above, or answer the questions below.
1. Why waste was sent to China
2. What type of waste?
3. When did China introduce the ban?
4. Why did it introduce the ban?
5. How has the ban impacted on the flow of waste?
**Complete one of the two options below - update March 2022**
Resource Security, Pathways & Politics... Option 1
|
You will have seen plenty in the news about Venezuela in recent months (March 2020) and the political struggles within the country. You will also know that Venezuela has the largest oil reserves in the world. So, how can it be that a country it spiraling into decline despite having such large natural resource wealth. The excellent article below breaks down the key issues that the country faces and why 'having all your eggs in one basket' is a dangerous economic policy.
Task - Read the article carefully and make notes on the economic and geopolitical issues surrounding this 'petrostate' using the worksheet below. |
|
Resource Security, Pathways & Politics... Option 2
Nord Stream 2 is a 1,234-km natural gas pipeline from Russia to Germany running through the Baltic Sea, financed by Gazprom and several European energy companies. It was started in 2011 to expand the Nord Stream line and double annual capacity to 110 billion m³ (source Wikipedia)
Task 1 - What is Nord Stream 2?
Watch the B1M video below and outline how the project was planned and why Ukraine was being bypassed. What were the controversies behind the scheme?
Task 1 - What is Nord Stream 2?
Watch the B1M video below and outline how the project was planned and why Ukraine was being bypassed. What were the controversies behind the scheme?
Task 2 - Russian Leverage?
Why was the USA worried about how the pipeline might give Russia leverage over Europe? Watch the first 3:35 of the video below and take notes on key gas 'reliance' data in Europe.
Task 2 - Russian Leverage?
Why was the USA worried about how the pipeline might give Russia leverage over Europe? Watch the first 3:35 of the video below and take notes on key gas 'reliance' data in Europe.
Task 3 - When geopolitics & sport mix.
Find out what the term 'soft power' means. Write that definition down. Now, watch the Vox video below and make notes on why Gazprom/Russian government exerted soft power in the world of football
On 24 February 2022, Russia began a military invasion of Ukraine, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian conflict that began in 2014. Internationally considered a war of aggression, it is the biggest assault on a European state since World War II. The invasion has caused the largest refugee crisis in Europe since World War II, with over 3.3 million Ukrainians fleeing their country since the start of war.
Task 4 - Watch the video below and make a note of the German response to the invasion of Ukraine by Russia in terms of the German approval of the NS2 pipeline. Include notes on the views of the USA and Ukraine in the matter.
Task 4 - Watch the video below and make a note of the German response to the invasion of Ukraine by Russia in terms of the German approval of the NS2 pipeline. Include notes on the views of the USA and Ukraine in the matter.
Task 5 - Watch the short video below and take notes on what happened. Now conduct some research to find out who the most likely suspects were and why they would do this.
Task 6 - Using this link, outline the response of the EU to Russian energy supplies (possibilities) and include at least two charts to show this trend.