What you'll need to know...
KEY CONCEPT - How different places become interconnected by global interactions
An overview of contemporary global networks and flows:
• global trade in materials, manufactured goods and services
• an overview of international aid, loans and debt relief
• international remittances from economic migrants
• illegal flows, such as trafficked people, counterfeit goods and narcotics
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and outsourcing by transnational corporations (TNCs), and ways in which this networks places and markets
• Two contrasting detailed examples of TNCs and their global strategies and supply chains
Synthesis, evaluation and skills opportunities
The relative importance of different flows, and the suitability of different methods for graphically representing flows and interactions
An overview of contemporary global networks and flows:
• global trade in materials, manufactured goods and services
• an overview of international aid, loans and debt relief
• international remittances from economic migrants
• illegal flows, such as trafficked people, counterfeit goods and narcotics
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and outsourcing by transnational corporations (TNCs), and ways in which this networks places and markets
• Two contrasting detailed examples of TNCs and their global strategies and supply chains
Synthesis, evaluation and skills opportunities
The relative importance of different flows, and the suitability of different methods for graphically representing flows and interactions
Global Trade in Materials, Manufactured Goods & Services...
Trade in Goods
Task 1 - Click here to be taken to the OECD (remember the work from the previous module) page on Global Trade. Define (simply) 'Trade in Goods'.
Task 1 - Click here to be taken to the OECD (remember the work from the previous module) page on Global Trade. Define (simply) 'Trade in Goods'.
Task 2 - Using a copy of the graph above, describe the global pattern in the trade of goods. Make reference to G7, G20 and a comparison between the E.U and PRC.
Trade in Services
Task 3 - Using this OECD website page, define 'Trade in Services'.
Task 4 - Using a copy of the graph above, describe the global pattern in the trade of services. Make reference to G7, G20 and a comparison between the E.U and PRC.
Task 5 - State the trade type that has greater financial importance globally.
Raw Materials
Task 6 - Watch the video below and take notes on how trade in raw materials is important for economic growth and how restrictive export policies can negatively impact development in mineral-rich economies
Task 5 - State the trade type that has greater financial importance globally.
Raw Materials
Task 6 - Watch the video below and take notes on how trade in raw materials is important for economic growth and how restrictive export policies can negatively impact development in mineral-rich economies
Task 7 - Spend a little time using the interactive map below. This shows countries who produce, have reserves of and export a variety of raw materials.
Choose a crucial raw material from the menu on the top right hand side to see the spatial distribution and amount produced by each country. Together with a screenshot of the map, comment on the spatial distribution of the countries who trade in this resource.
Task 8 - Power Struggle. Watch both of the videos below. Take notes on why the tariffs have been imposed by the USA on aluminium and steel imports and what the retaliatory measures have been by those affected.
|
|
|
An overview of international aid, loans and debt relief...
With the advancement of global interactions, populations around the world are now more aware than ever of the disparity that exists between the wealthy and the poor. Whilst it is true to say that most people in the world live in MIC's and wealth is increasing, nearly 700 million people still live below the poverty line, earning less than $1.90 per day. You can see the state of play today by examining this Gapminder chart.
Celebrity Activism?
Back in 1985, a series of concerts called 'Live Aid' were planned and broadcast in response to the humanitarian tragedy unfolding in Ethiopia. This news report from the BBC (warning of upsetting images) was broadcast around the world and stirred key figures in music industry and in government into action to raise money. The events in London, Paris and New York were broadcast around the world on television and raised close to $130 million. This was the first example of a 'celebrity driven' international aid drive and many more have taken place since.
Fast forward to 2005 and the Live 8 concerts that were timed to precede the G8 conference and summit held in Scotland from 6–8 July. Both events also coincided with the 20th anniversary of Live Aid. Run in support of the aims of the UK's Make Poverty History campaign and the Global Call to Action Against Poverty, ten simultaneous concerts were held on 2 July and one on 6 July. On 7 July, the G8 leaders pledged to double 2004 levels of aid to poor nations from US$25 billion to US$50 billion by the year 2010. Half of the money was to go to Africa. More than 1,000 musicians performed at the concerts, which were broadcast on 182 television networks and 2,000 radio networks. This time, pledges of aid were also complimented by pledges to reduce unsustainable debt levels (debt relief).
Celebrity Activism?
Back in 1985, a series of concerts called 'Live Aid' were planned and broadcast in response to the humanitarian tragedy unfolding in Ethiopia. This news report from the BBC (warning of upsetting images) was broadcast around the world and stirred key figures in music industry and in government into action to raise money. The events in London, Paris and New York were broadcast around the world on television and raised close to $130 million. This was the first example of a 'celebrity driven' international aid drive and many more have taken place since.
Fast forward to 2005 and the Live 8 concerts that were timed to precede the G8 conference and summit held in Scotland from 6–8 July. Both events also coincided with the 20th anniversary of Live Aid. Run in support of the aims of the UK's Make Poverty History campaign and the Global Call to Action Against Poverty, ten simultaneous concerts were held on 2 July and one on 6 July. On 7 July, the G8 leaders pledged to double 2004 levels of aid to poor nations from US$25 billion to US$50 billion by the year 2010. Half of the money was to go to Africa. More than 1,000 musicians performed at the concerts, which were broadcast on 182 television networks and 2,000 radio networks. This time, pledges of aid were also complimented by pledges to reduce unsustainable debt levels (debt relief).
Starter: Watch the first 10 minutes of The Band Aid Story - 2004 below. Then, watch the second video below (click 'watch on YouTube' link). Note the difference between 1984 & 2015*. 1984 could be considered the first time that a collective international aid effort was launched between Europe / USA and a poor and impoverished nation, Ethiopia.
Band Aid, and the related Live Aid concerts, raised over $100m for the Ethiopian famine victims. They galvanised a public that had largely been indifferent, marking a watershed for how celebrities engaged with humanitarian issues and how organisations conducted fundraising appeals. However, with unfounded and inaccurate lyrics, the Christmas song not only created misconceptions about Ethiopia, but it did so in a patronising way.
Despite the fact the famine was localised to northern Ethiopia and a result of political manipulation, the songs, concerts, and fundraising appeals perpetuated a single, negative, and distorted view of Ethiopia, making it synonymous with famine, poverty, and desperation. (Al Jazeera 2013)
*Note that recent civil unrest in Ethiopia in north of the country that have caused severe disruption to the country and its development.
|
|
|
|
|
|
International Aid
Task 1 - Define International Aid, Bilateral Aid and Multilateral Aid.
Task 2 - Watch the third video above on 'Foreign Aid' and make notes on the content.
Task 3 - Watch the fourth video above on the 'Problem with Foreign Aid' and make notes on why this can be problematic.
Task 4 - Now click on a recent news story below, print out and highlight the key information within. Focus on the reasons why the UK feels it needs to reduce its aid budget in 2020.
International Loans
Task 5 - Watch the first video beneath and take notes on why the IMF (remember this from previous lessons) lends money. Give examples of the factors that require countries to ask for assistance.
Task 5 - Watch the first video beneath and take notes on why the IMF (remember this from previous lessons) lends money. Give examples of the factors that require countries to ask for assistance.
Task 6 - The IMF are constantly processing requests for emergency loans especially given the havoc that COVID-19 is wreaking on economies around the world. Click here to be taken to a Google search of news recent stories linked to IMF lending. Choose one example from the list and write a 100 word summary of the loan situation in that country.
Debt Relief
Task 7 - Watch the video beneath and make notes on the benefits of debt relief programmes.
Task 8 - Outline briefly the HIPC initiative. This page will help you.
Task 9 - Read this article carefully and comment on the spatial distribution (place) of countries that have received substantial debt relief.
Task 7 - Watch the video beneath and make notes on the benefits of debt relief programmes.
Task 8 - Outline briefly the HIPC initiative. This page will help you.
Task 9 - Read this article carefully and comment on the spatial distribution (place) of countries that have received substantial debt relief.
International remittances from economic migrants...
Task 1 - Watch the video below to recap on what remittances are and why they are vital to economies around the world. Now study the map below to get an overview of the countries that rely on remittance income. The really famous example of this is USA - Mexico transfer of money but as you can see, it is by no means the only example. Why and where does 31% of the Nepalese GDP come through remittances?
Click on this link to be taken to an interactive remittances map (2016). It is set to default to show the payments to/from the USA but using the drop down menu, you can change the country. For IST students, choose France to see the transfer of money to and from the country.
Task 2 - Using a screen shot of the map above (interactive version here) describe the spatial pattern of remittance inflow (as a % of GDP). Now using the link above, choose your home country take screen shots of inflows and outflows and explain the key patterns of remittance flows. Can you spot any major flows that have historical or geographic significance?
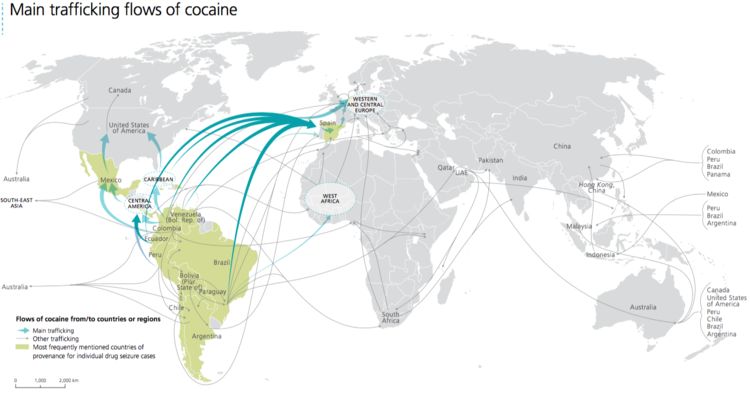
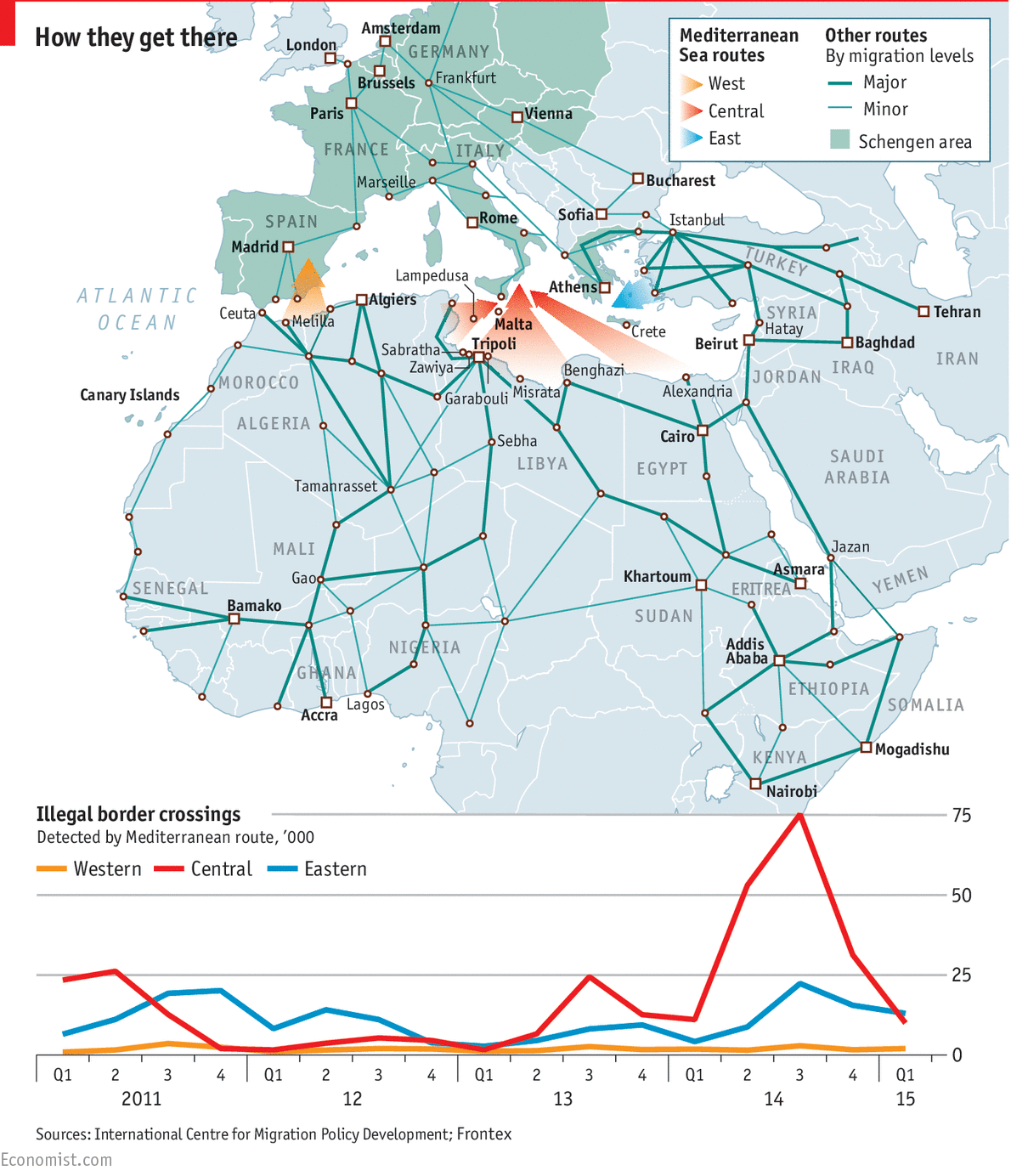
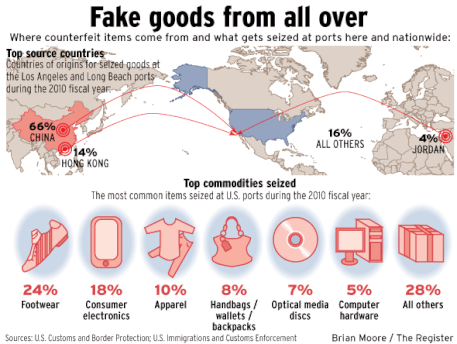
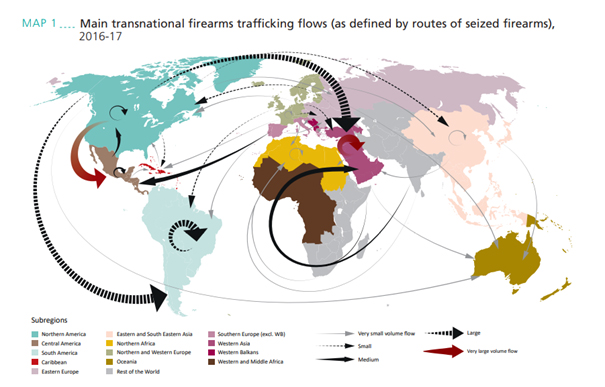
Illegal Flows...
You will be completing this piece of work as a group presentation exercise. Each person / group will be given one of the following four illegal flows to study and research.
Please use the evidence board below to produce a 5 minute presentation along with a 1 sided A4 factsheet about the allocated illegal flow.
Please use the evidence board below to produce a 5 minute presentation along with a 1 sided A4 factsheet about the allocated illegal flow.
Case Study 1 - Narcotics - El Naya - Cocaine Highway to the USA
Case Study 2 - People Smugglers Africa to Europe
Case Study 3 - Counterfeit Trainers into USA
Case Study 4 - Illegal Animal Trade
Case Study 5 - Illegal Firearms Trade
FDI & outsourcing by transnational corporations (TNCs)...
What is 'Foreign Direct Investment - FDI'?
Foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment made by a firm or individual in one country into business interests located in another country. Generally, FDI takes place when an investor establishes foreign business operations or acquires foreign business assets, including establishing ownership or controlling interest in a foreign company.
What is 'Outsourcing'?
Outsourcing is the business practice of hiring a party outside a company to perform services and create goods that traditionally were performed in-house by the company's own employees and staff. Usually done as a cost-cutting measure, it can affect jobs ranging from customer support to manufacturing to the back office.
(Source: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/fdi.asp#ixzz5SKrPtC2Y)
Foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment made by a firm or individual in one country into business interests located in another country. Generally, FDI takes place when an investor establishes foreign business operations or acquires foreign business assets, including establishing ownership or controlling interest in a foreign company.
What is 'Outsourcing'?
Outsourcing is the business practice of hiring a party outside a company to perform services and create goods that traditionally were performed in-house by the company's own employees and staff. Usually done as a cost-cutting measure, it can affect jobs ranging from customer support to manufacturing to the back office.
(Source: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/fdi.asp#ixzz5SKrPtC2Y)
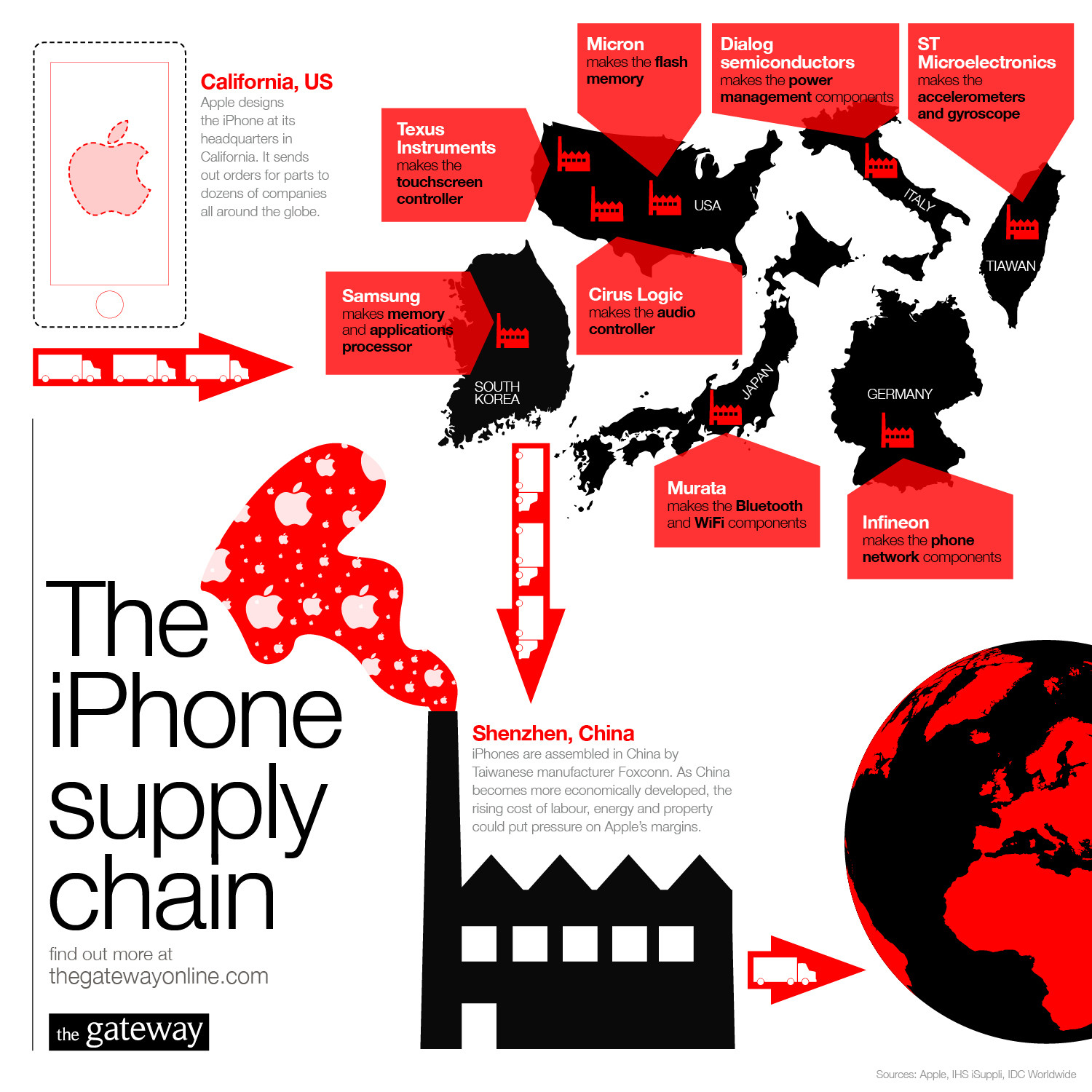
Case Study - Apple "Designed by Apple in USA, Assembled in China"
|
Task 1 - Where does you phone come from? Watch the Economist video to the right and takes notes. Task 2 - What is outsourcing and why some HICs aren't keen on it. Define outsourcing. Then watch the second video below (AP) and makes notes on why former President, Donald Trump was not a fan of it! Mr Trump preferred an option where Apple would commit to making more phones in the United States. Watch the third video (WSJ) and explain why it is not quite as simple as re-sourcing jobs to the States. Task 3. Outline the main features of the newest iPhone or iPad. What makes them so different to the competition (Android, HTC etc)? Why are they so expensive? The last video (below) will help. You might want to watch some of the Apple promo video in video 5 below. Primary Resource for Task 4&5 - From Mac World 17 Feb 2017 Task 4. Outline the reasons for iPad and iPhone production in China. Why has Apple manufacturing been internationally outsourced from the USA? Use this resource to help you. Why does Tim Cook (Apple CEO) say that their products are made in China? Link here. Task 5. What are the social and economic issues (positive and negative) associated with the global Apple production process? Watch this CNN news report Task 6 - Responses to outsourcing by Donald Trump. Click on this Sep 2018 Vox article to read about the issues caused by USA's trade war on/with Apple. Make notes on the content and what Trump is hoping Apple will eventually do. |
|
TNCs and their global strategies and supply chains...
Two detailed case studies are required here of two contrasting TNC's including their global strategy and supply chains. For this unit of work, we will be splitting into two groups and analysing both Apple (USA & High Tech) and Starbucks (USA Food & Drink).
Starter Task
Define: TNC
Define: Global Strategy
Define: Supply Chain
Task 1 - Split into two groups. One group will be researching Apple and the other Starbucks. Both are well known TNC's and the chances are that you have been consumers of their product range.
Use the video wall beneath to build up a picture of the history of the companies, their global/local strategies as well as their supply chains.
You are going to produce a 5-10 minute presentation to give to your peers using PowerPoint, Prezzie etc.
Slide 1 - Introduction / logo / group details / quote about the TNC
Slide 2 - Brief history and major product release dates (Starbucks history)
Slide 3 - Global / local strategies
Slide 4 - Supply chains
Slide 5 - 4P's summary
Slide 6 - Connecting people and places.
Slide 7 - Synthesis - links with one other area of the IB DP Geog course.
Starter Task
Define: TNC
Define: Global Strategy
Define: Supply Chain
Task 1 - Split into two groups. One group will be researching Apple and the other Starbucks. Both are well known TNC's and the chances are that you have been consumers of their product range.
Use the video wall beneath to build up a picture of the history of the companies, their global/local strategies as well as their supply chains.
You are going to produce a 5-10 minute presentation to give to your peers using PowerPoint, Prezzie etc.
Slide 1 - Introduction / logo / group details / quote about the TNC
Slide 2 - Brief history and major product release dates (Starbucks history)
Slide 3 - Global / local strategies
Slide 4 - Supply chains
Slide 5 - 4P's summary
Slide 6 - Connecting people and places.
Slide 7 - Synthesis - links with one other area of the IB DP Geog course.
|
“Our whole goal in life is to give you something you didn’t know you wanted and then once you get it, you can’t imagine your life without it… and you can count on apple doing that.”
Tim Cook History of Apple
Global Strategy - Offshore Profits & Outsourcing
Offshoring: Offshore investment is the keeping of money in a jurisdiction other than one's country of residence. ... Poorly regulated offshore domiciles have served historically as havens for tax evasion, money laundering, or to conceal or protect illegally acquired money from law enforcement in the investor's country.
Outsourcing: Outsourcing is the business practice of hiring a party outside a company to perform services and create goods that traditionally were performed in-house by the company's own employees and staff. Apple Supply Chain - Designed in California, Manufactured in China
|
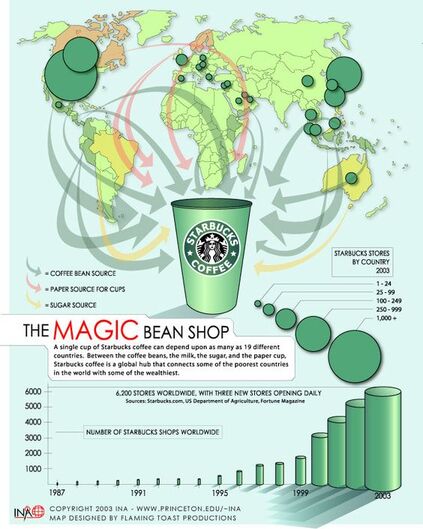
“Starbucks being an extension of peoples home and work. The sense of community, human connection. That appears to be as relevant in Turkey, China, Japan and Spain as it is here in America. And Starbucks I think is creating something for people all over the world that has not existed before.” -- Howard Schultz
History of Starbucks
Global Strategy - Regional Glocalisation of Products
Global Strategy: What a company takes when it wants to compete and expand in the global market. A global strategy refers to the plans an organization has developed to target growth beyond its borders. Specifically, it aims to increase the sales of goods or services abroad.
Glocalisation: Glocalization is a combination of the words "globalization" and "localization." The term is used to describe a product or service that is developed and distributed globally but is also adjusted to accommodate the user or consumer in a local market. Starbucks Supply Chain Information
Update to the infographic above: Total stores: 30,000 across 80 markets (as of June 30, 2019)
|
When the global strategy doesn't work ......
|
|
|