What you'll need to know...
KEY CONCEPT - How global interactions create environmental risks for particular places and people
Transboundary pollution (TBP) affecting a large area/more than one country
• One TBP case study including the consequences and possible responses
Environmental impacts of global flows at varying scales:
• localized pollution, including impacts along shipping lanes
• carbon footprints for global flows of food, goods and people
Environmental issues linked with the global shift of industry:
• polluting manufacturing industries
• food production systems for global agribusiness
Synthesis, evaluation and skills opportunities
How global interactions affect the physical environment by varying degrees at different scales
Transboundary pollution (TBP) affecting a large area/more than one country
• One TBP case study including the consequences and possible responses
Environmental impacts of global flows at varying scales:
• localized pollution, including impacts along shipping lanes
• carbon footprints for global flows of food, goods and people
Environmental issues linked with the global shift of industry:
• polluting manufacturing industries
• food production systems for global agribusiness
Synthesis, evaluation and skills opportunities
How global interactions affect the physical environment by varying degrees at different scales
Transboundary Pollution Event...
|
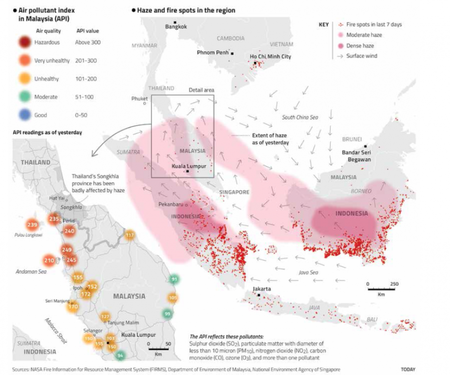
Southeast Asian haze is a fire-related large-scale air pollution problem that occurs regularly. These haze events have caused adverse health and economic impact on Brunei Darussalam, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, and to a lesser degree, the Philippines and Thailand. The problem flares up every dry season, in varying degrees. Transboundary haze in Southeast Asia has been recorded since 1972.
The haze is largely caused by illegal agricultural fires due to industrial-scale slash-and-burn practices in Indonesia, especially from the provinces of South Sumatra and Riau in Indonesia's Sumatra island, and Kalimantan on Indonesian Borneo. Burned land can be sold at a higher price illegally, and eventually used for activities including oil palm and pulpwood production. Burning is also cheaper and faster compared to cutting and clearing using excavators or other machines. Task 1 - Using the resources above and below, create a piece of commentary that explains i. how global interactions causes pollution that transcends political boundaries. ii. the consequences of this transboundary pollution event iii. the responses to the event by key stakeholders. |
|
|
|
|
|
We are also going to complete a piece of analysis here that allows us to complete a syllabus point that occurs a little later in this unit. The syllabus point is:
'Environmental issues linked with the global shift of industry - food production systems for global agribusiness'
Clearly, unregulated Palm Oil production, on top of being partly to blame for this TBP event, also links in to food production systems and is big agri-business. You have seen the wider atmospheric environmental issues caused by this burning and we will now take a look at the impacts on biodiversity as well as the alternatives.
'Environmental issues linked with the global shift of industry - food production systems for global agribusiness'
Clearly, unregulated Palm Oil production, on top of being partly to blame for this TBP event, also links in to food production systems and is big agri-business. You have seen the wider atmospheric environmental issues caused by this burning and we will now take a look at the impacts on biodiversity as well as the alternatives.
Task 2 - Listen to the Podcast above
Why can Palm Oil be seen to have a bad press?
Which animal has traditionally been associated with palm oil destruction?
What other crops are perhaps overlooked in terms of their environmental impacts?
Why can biodiversity still be maintained in the oil plantations above other crop type?
Task 3 - Read
Click here to access a 2018 article from 'The Conversation'.
Make notes on the reasons why a ban on palm oil could result in the destruction of even more rainforest and reduction of biodiversity and link this in to soy bean production.
Task 4 - The Infographic Task
Click here to access an infographic showing the production, use and factors influencing supply and demand of Palm Oil with a focus on Malaysia.
i. Who controls the largest distribution of Palm Oil planted areas in Malaysia?
ii. What is the total value of Palm Oil (RM) to Malaysia?
iii. Explain why topical areas are ideal for the growth and cultivation of Palm Oil.
iv. How does dry weather in the U.S impact on Palm Oil production in Malaysia?
v. State one weakness and one improvement that you would make to this graphic.
Localized pollution along shipping lanes...
Shipping containers and container ships are responsible for the transport and distriubution of an extremely high percentage of consumer goods around the planet. For example, in Australia, they account for 99% of the total merchandise trade. This extremely cost effective way of moving non-perishable manufactured goods from South East Asia to the rest of the world has led to more complex supply chains and ultimately cheaper costs passed on to the consumer.
You can see from the map below that high concentrations of ships travel through some well known and frequented shipping passages and chokepoints (Suez, Panama). This PDF map shows you that there are potentially an infinite number of maritime shipping routes that can be used for commercial circulation, but the configuration of the global system is relatively simple. The main axis is a circum-equatorial corridor linking North America, Europe and Pacific Asia through the Suez Canal, the Strait of Malacca and the Panama Canal.
You can see from the map below that high concentrations of ships travel through some well known and frequented shipping passages and chokepoints (Suez, Panama). This PDF map shows you that there are potentially an infinite number of maritime shipping routes that can be used for commercial circulation, but the configuration of the global system is relatively simple. The main axis is a circum-equatorial corridor linking North America, Europe and Pacific Asia through the Suez Canal, the Strait of Malacca and the Panama Canal.
Created by London-based data visualisation studio Kiln and the UCL Energy Institute
|
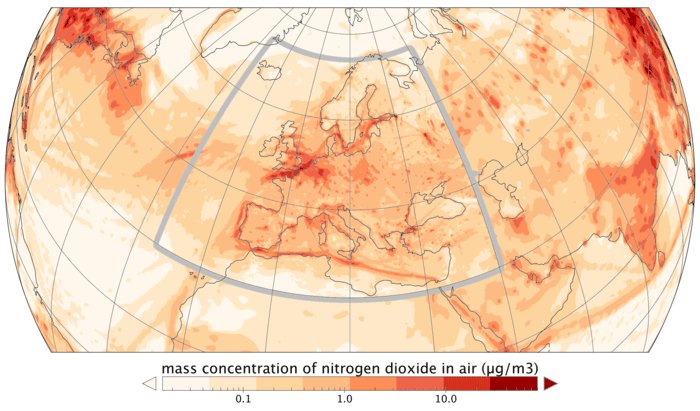
Task 1 - Describe the global distribution of shipping lanes Task 2 - Listen to this Podcast and answer the following questions: a. How many t-shirts could fit into one container box b. How many containers can the container ship in the report hold? c. Outline how shipping worked in pre-container days. d. What were the key benefits of containers and how did this ultimately lead to job losses? e. To what extent could it be argued that the container has been a major facilitator of globalization? Task 3 - Is correlation causation? Study the map to the right carefully. It shows mass concentration of nitrogen dioxide in the air. Using the interactive visual above and this map, outline the possible links between the shipping industry and air pollution. Further information can be found here. |
Synthesis & links to other parts of the specification.
In a 12 mark specific question on paper 3 that might link to this section of the HL course, you would be required to use one more example. This would come in the the form of Global Resource Consumption & Security section of Perspectives.
The question could state:
Using examples, analyses the human impact of the environmental consequences of the global flows of resources and materials. 12
We studied the impacts of e-waste on Ghana as well as the rejection of recycled waste by the Chinese government. This of course fits nicely with environmental impacts of global flows of e-waste / recycling.
Here is the link to the section of the website where we completed that work (near the bottom of the page)
In a 12 mark specific question on paper 3 that might link to this section of the HL course, you would be required to use one more example. This would come in the the form of Global Resource Consumption & Security section of Perspectives.
The question could state:
Using examples, analyses the human impact of the environmental consequences of the global flows of resources and materials. 12
We studied the impacts of e-waste on Ghana as well as the rejection of recycled waste by the Chinese government. This of course fits nicely with environmental impacts of global flows of e-waste / recycling.
Here is the link to the section of the website where we completed that work (near the bottom of the page)
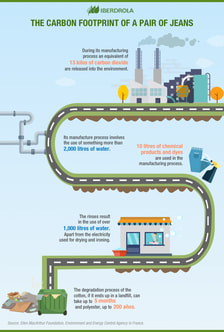
Carbon footprints for global flows of food, goods and people...
Your task here is to take notes whilst researching carbon footprints of the flows of food, goods and people. Your aim is to be able to answer the following Paper 3 question:
Using examples, contrast the carbon footprint of different global flows. [12]
Contrast: Give an account of the differences between two (or more) items or situations, referring to both (all) of them throughout.
To start with, check out the first video below to help you to understand what a Carbon Footprint is and how it is calculated.
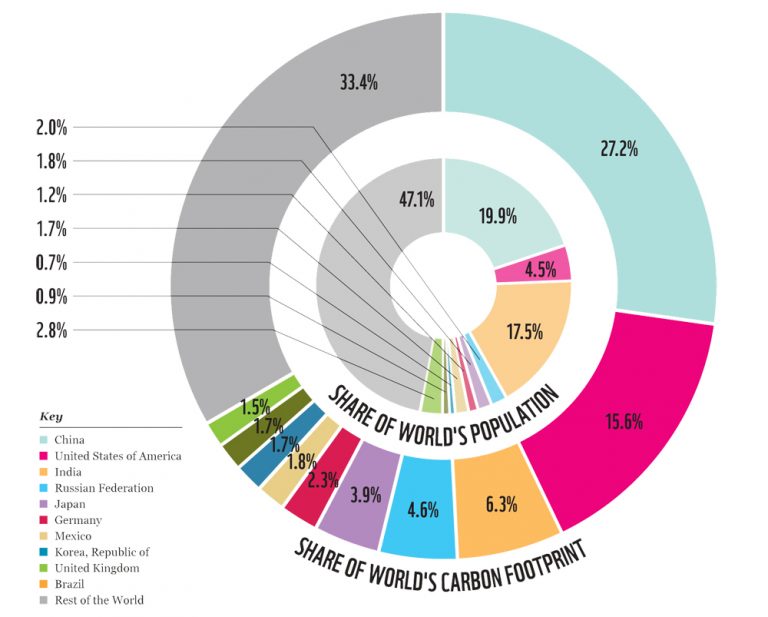
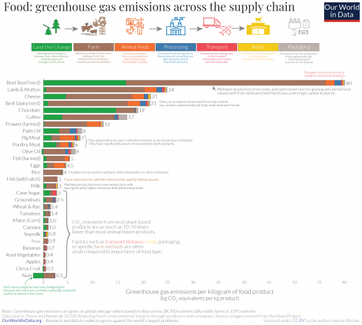
Now check out the visual below. Study it carefully as it contains two sets of important data to consider.
Using examples, contrast the carbon footprint of different global flows. [12]
Contrast: Give an account of the differences between two (or more) items or situations, referring to both (all) of them throughout.
To start with, check out the first video below to help you to understand what a Carbon Footprint is and how it is calculated.
Now check out the visual below. Study it carefully as it contains two sets of important data to consider.
Part 1 - Food
Part 2 - Goods
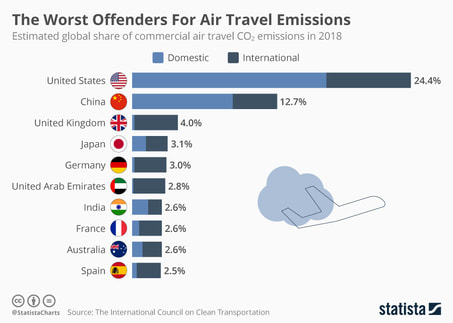
Part 3 - Flow of people (planes)
Alternatively, you can use Richard Allaway's excellent geographyalltheway.com site. Please click on the icon above to access the page (subscription required). Complete the tasks and exam question set out.
Environmental issues linked with the global shift of polluting manufacturing industries...
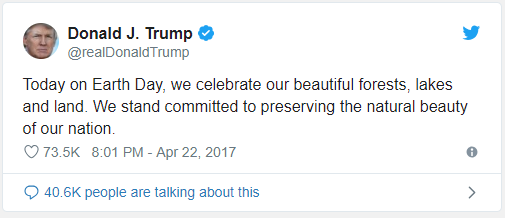
Above are two tweets written by President Donald Trump within three hours of each other in April 2017.
1. What do you think was said in response to the first tweet that merited the President tweeting for a second time?
2. How could economic growth lead to enhanced environmental protection?
Study the Kuznet Curve below. This plots level of economic development/growth against level of environmental degradation.
3. Produce a 100 word summary of this model with explanations for the trends shown.
4. To what extent was Donald Trump's tweet correct when talking about the USA?
5. Could the current Prime Minister of Ethiopia, Abiy Ahmed, make the same claim in 2022?
1. What do you think was said in response to the first tweet that merited the President tweeting for a second time?
2. How could economic growth lead to enhanced environmental protection?
Study the Kuznet Curve below. This plots level of economic development/growth against level of environmental degradation.
3. Produce a 100 word summary of this model with explanations for the trends shown.
4. To what extent was Donald Trump's tweet correct when talking about the USA?
5. Could the current Prime Minister of Ethiopia, Abiy Ahmed, make the same claim in 2022?
Read this article from The Conversation and take notes on the following:
1. What does the 'greening of manufacturing' refer to?
2. What does 'brown imports' mean?
3. What % of pollutants emitted in China is caused by the production of goods for the export market / USA?
4. What does the term 'offshoring' refer to?
5. Outline how some HIC manufacturers keep the "dirty" segment of their production process away from their home.
6. What is the suggested relationship between the outsourcing of dirty manufacturing awy from the USA and toxic air emissions from manufacturing in the USA?
7. What drives the outsourcing of pollution manufacturing away from the USA?
8. Why is this polluting manufacturing accepted in some poor countries?
1. What does the 'greening of manufacturing' refer to?
2. What does 'brown imports' mean?
3. What % of pollutants emitted in China is caused by the production of goods for the export market / USA?
4. What does the term 'offshoring' refer to?
5. Outline how some HIC manufacturers keep the "dirty" segment of their production process away from their home.
6. What is the suggested relationship between the outsourcing of dirty manufacturing awy from the USA and toxic air emissions from manufacturing in the USA?
7. What drives the outsourcing of pollution manufacturing away from the USA?
8. Why is this polluting manufacturing accepted in some poor countries?