KEY CONCEPT - How economic and demographic processes bring change over time to urban systems
Urbanization & natural increase & centripetal population movement, including
Centrifugal population movements, including
3. Urban system growth including infrastructure improvements over time, such as transport, sanitation, water, waste disposal and telecommunications
4. The causes of urban deindustrialization and its economic, social and demographic consequences
Urbanization & natural increase & centripetal population movement, including
- rural–urban migration in industrializing cities
- inner city gentrification in post-industrial cities
Centrifugal population movements, including
- suburbanization
- counter-urbanization
3. Urban system growth including infrastructure improvements over time, such as transport, sanitation, water, waste disposal and telecommunications
- Case study of infrastructure growth over time in one city
4. The causes of urban deindustrialization and its economic, social and demographic consequences
Urbanization & Natural Increase...
Urbanization is perhaps one of the most important geographic processes at work today. Back in 2008, a tipping point was reached. For the first time in human history, more people lived in urban areas than in rural areas. You have previously studied the impacts of the growth of mega cities (over 10 million inhabitants) and have seen first hand some of the issues that are caused by the swelling of urban areas. For IST students here in Toulouse and in other cities around the world, that is best seen with the traffic congestion and relentless building on the green belt to keep pace with the additional arrivals into the city every year.
Urbanization is defined as the "proportion of people living in built environments such as towns and cities". The word proportion in this definition is very important, because it indicates that we must judge urbanization by looking at both the numbers of people living in both rural AND urban areas. (source: coolgeography)
Task 1 - This is a recap for you. Watch the following TED ED video and then answer the questions below. This work is taken from the excellent TED ED lesson here.
Urbanization is defined as the "proportion of people living in built environments such as towns and cities". The word proportion in this definition is very important, because it indicates that we must judge urbanization by looking at both the numbers of people living in both rural AND urban areas. (source: coolgeography)
Task 1 - This is a recap for you. Watch the following TED ED video and then answer the questions below. This work is taken from the excellent TED ED lesson here.
a. In 3-4 sentences, discuss the importance of improvements in farming techniques to the development of cities.
b. Reliable food supplies allowed humans the luxury of free time, which provided the opportunity to produce items for trade. Describe how the production of goods contributed to the growth of cities.
c. Experts predict that global population will top out around 10 billion people, with 7 billion of those people living in cities. What are some of the opportunities and challenges that cities will face as the population increases?
d. What percentage of the human population lived in cities 100 years ago?
* 10%
* 20%
* 40%
* 80%
e. Which of the below technologies is a development that resulted from the desire to trade with neighboring communities?
* The plow
* Walled cities
* Roads
* Water Distribution
f. What led to the development of the first semi-permanent settlements?
* Changes in the global climate
* An increase in freshwater supplies
* Improvements in healthcare
* Advances in agriculture
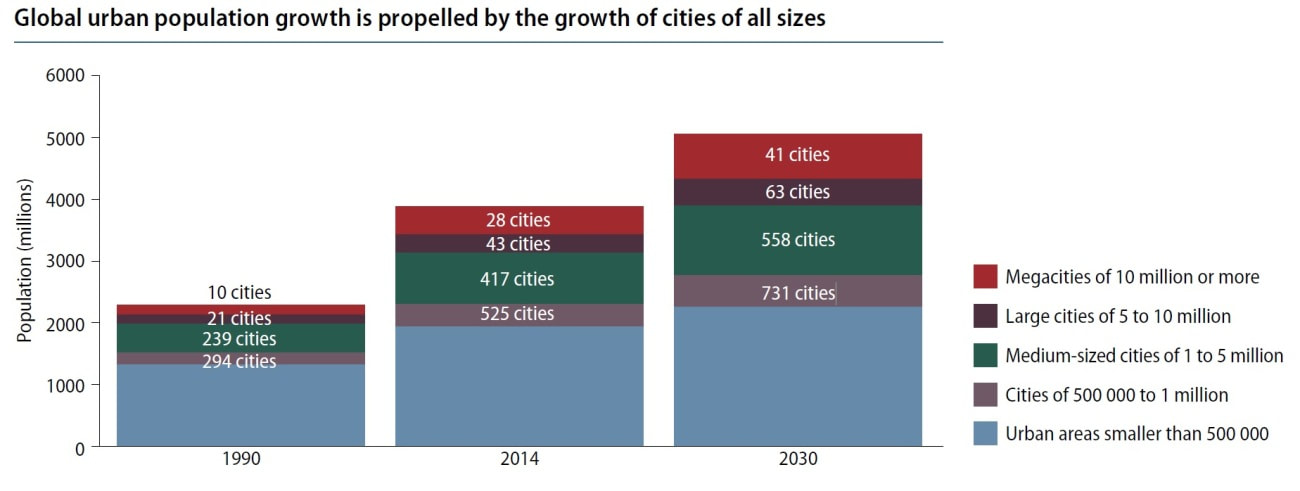
Task 2 - Study the graphic below. Pay attention to the key and the Y-axis. Using a copy of this graph, comment on the trends of urban growth from 1990 to 2030 (predicted).
Download the press release below that provides the headline facts and figures from the UN World Urbanization Prospects 2018 report.
Task 3 - Using a highlighter, extract the key data, paying particular attention to 'Place' & 'Possibility'.
Task 4 - Make a note of the following information:
Urbanization levels are affected by two key factors – Migration and Natural increase. We will cover migration elsewhere in the course but is worth noting the relevance of natural increase to the process of urbanization before we go on any further.
Natural Increase also has a major effect on rates of urbanization. During the initial urbanization phase natural increase in poorer parts of the world can increase as death rates fall in cities as people have;
· Better access to medical care
· Improved water supplies
· Sanitary conditions
· Improved wealth so improved food supply
Birth rates take longer to fall and indeed more babies survive as infant mortality falls in cities. Also, young people move to towns and cities, which also boosts the birth rate. These combined factors can fuel the rate of urbanization.
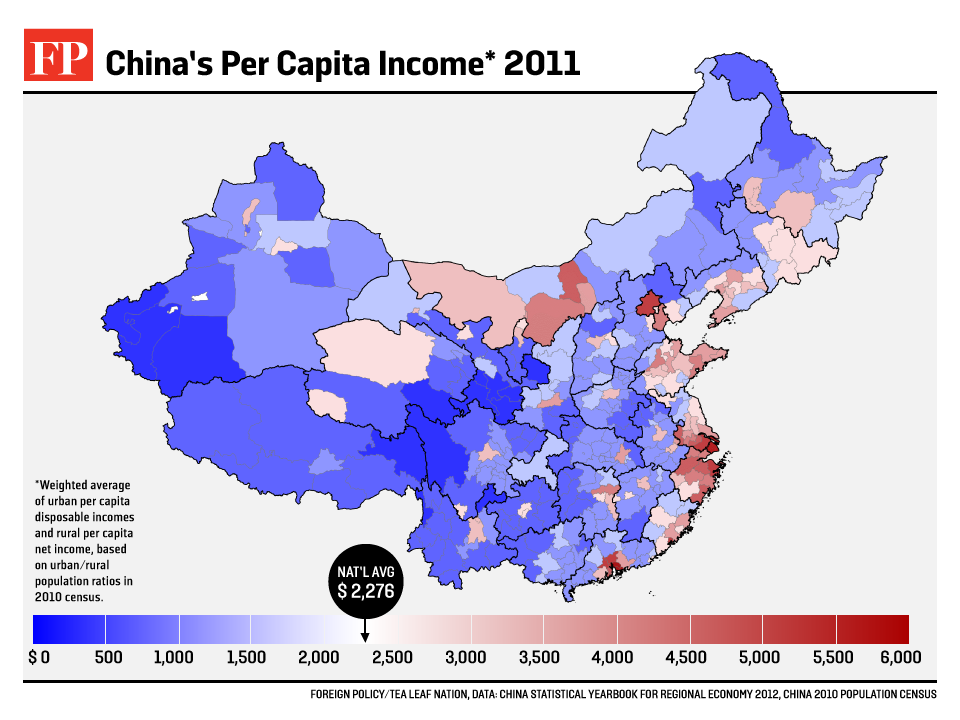
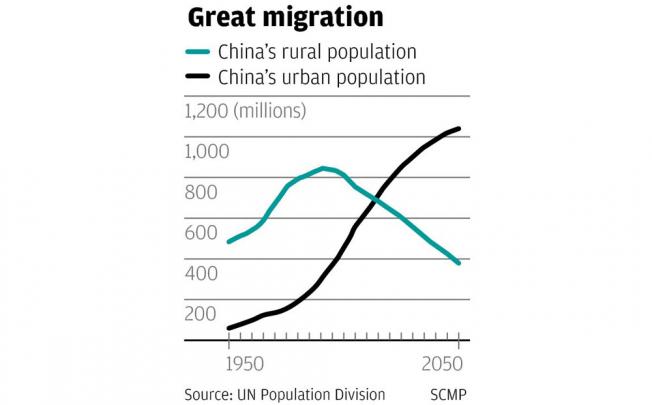
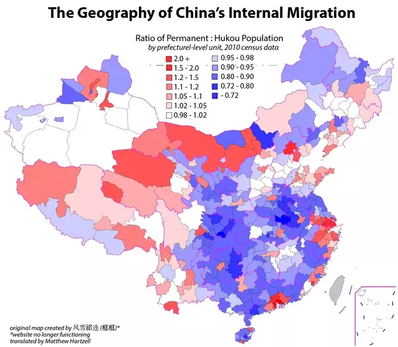
Rural to Urban Migration - Focus on China...
A centripetal movement is a movement of people towards a centre and that includes both pull and push factors.
Task 1 - Use the evidence board below to create a one page summary sheet that outlines the issues caused by rural to urban migration in Chinese cities. You should aim to include the following:
Task 1 - Use the evidence board below to create a one page summary sheet that outlines the issues caused by rural to urban migration in Chinese cities. You should aim to include the following:
- Place, Process (push & pull factors), Power, Possibility
- 2 maps
- 2 graphs
- 1 quote
- Explanation of Hukou
|
|
|
|
Inner city gentrification in post-industrial cities...
The process of gentrification can have multiple perspectives based on a number of factors. Firstly, you need to understand what gentrification means. You should watch the first video below and then think of an example in your local city where this may be the case. Discuss with your teacher / peers.
So, these different perspectives can vary. Spend 15 minutes watching the two videos below and making notes on how attitudes vary between Berlin and New Jersey.
|
|
|
Note to International School of Toulouse students: This part of the course has been covered in your Internal Assessment and so needs no further development or case studies here.
For non IST students, please click on the tab below to be taken to our case study page on gentrification in Berlin, Germany. The work can be found 2/3 of the way down the page.
Suburbanization & Counter Urbanization...
A centrifugal movement is a movement of people away from a centre as a result of push and pull factors.
Task 1 - Using the resources below, complete the following activities:
a) What do you understand by the term 'counter-urbanization'?
b) What is the difference between counter-urbanization and sub-urbanization?
c) Why is counter-urbanization a feature of most HIC's?
d) Classify the reasons for counter-urbanization under the following headings:
• Social
• Technological
• Environmental
• Economic.
e) Classify the impacts of counter-urbanization under the headings:
• Social
• Environmental
• Economic.
Task 1 - Using the resources below, complete the following activities:
a) What do you understand by the term 'counter-urbanization'?
b) What is the difference between counter-urbanization and sub-urbanization?
c) Why is counter-urbanization a feature of most HIC's?
d) Classify the reasons for counter-urbanization under the following headings:
• Social
• Technological
• Environmental
• Economic.
e) Classify the impacts of counter-urbanization under the headings:
• Social
• Environmental
• Economic.
|
Sub-urbanization Resources
|
Counter-urbanization Resources
|
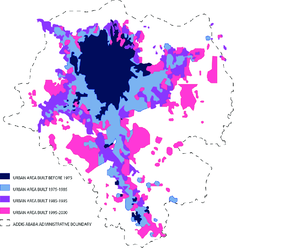
Infrastructure growth over time in Addis Ababa...
We have previously studied (in Option A) the impacts of the The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam on the population and economy of Ethiopia. We are going to now go back to the country to look at the growth of its capital city over time. Addis Ababa is one of the fastest growing cities in Africa and is prospering with direct foreign investment (particularly from China) and technological revolution that the government hopes with help the country to break into the MIC category by the year 2025.
Ethiopia is not a coastal country and understands the need to be connected to a port in order to facilitate the effective import and export of products and services. One recent Chinese funded operation has been the construction of the 600 KM Addis Ababa to Djibouti railway line (see second video below).
Your IB DP Paper 1 question is a follows:
Examine the patterns of urban infrastructure growth that have developed in one named city over time. [10]
You are going to be focusing on the following factors that have influenced the growth of Addis Ababa:
This is also a great example of global interactions as you will see that many of the projects below link Ethiopia to China.
Task 1 - Watch the three videos below to acquaint yourselves with the factors responsible for the growth of the city. Create a note taking frame using the five bullet points above as a starting point and leaving a space for the inclusion of one or more maps.
Ethiopia is not a coastal country and understands the need to be connected to a port in order to facilitate the effective import and export of products and services. One recent Chinese funded operation has been the construction of the 600 KM Addis Ababa to Djibouti railway line (see second video below).
Your IB DP Paper 1 question is a follows:
Examine the patterns of urban infrastructure growth that have developed in one named city over time. [10]
You are going to be focusing on the following factors that have influenced the growth of Addis Ababa:
- transport
- sanitation
- water
- waste disposal
- telecommunications
This is also a great example of global interactions as you will see that many of the projects below link Ethiopia to China.
Task 1 - Watch the three videos below to acquaint yourselves with the factors responsible for the growth of the city. Create a note taking frame using the five bullet points above as a starting point and leaving a space for the inclusion of one or more maps.
|
|
|
|
Overview of Urban Expansion
Task 2 - The third video above gives you an over view of the growth of the city from the early 1970's to 2016.
Additional Resources
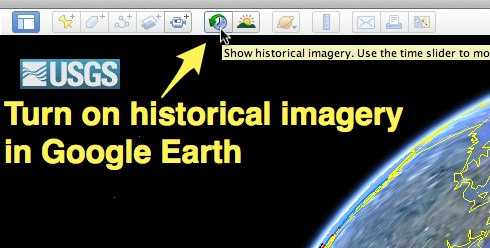
To compliment your study, you should launch the Google Earth App** to identify the five growth factors above from the most up to date map of the city. Once you are on Google Earth App, select the 'show historical imagery' button (see image example below) and slide back to 1973.
**If you only have access to Google Earth through your web browser, this function will not work. Please download the worksheet below that contains still images from Google Earth showing that growth over time.
You should also consult this interactive site (2010) specifically focusing on the section entitled 'Urban Extent'.
Infrastructure Growth
Task 3 - Click on the link below to access an article about the improvements in connecting Addis Ababa to the coastline to improve future trade. Highlight the key content that would be required to answer the IB DP Question stated at the top of this section.
Transport Growth
Task 4 - Click on the blue button below to access an excellent interactive study based around the Light Railway System in Addis Ababa.
Task 4 - Click on the blue button below to access an excellent interactive study based around the Light Railway System in Addis Ababa.
Water & Sanitation
Task 5 - Use the resources below to build up your notes on the issues facing Addis Ababa, its exploding population and its ability to keep pace with water supply and sanitation.
* - use the Ctrl F function to find the areas of the article relevant to Addis Ababa.
Telecommunications
There are many internet cafe's in Ethiopia but over 3/4 of them are located in Addis Ababa (see this map).
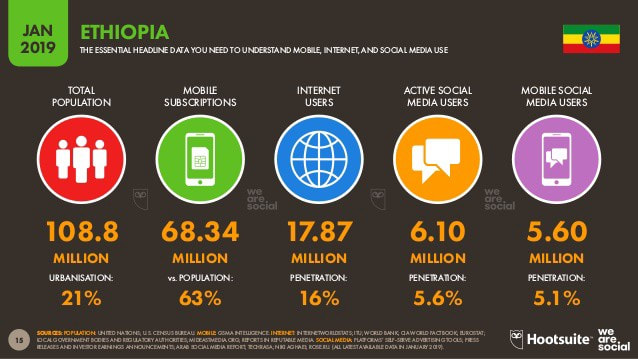
Take a look at the infographic below that details the internet use in Ethiopia (2019).
Now check out the information below that about the 4G internet launch in Addis Ababa.
Task 6 - Using the information in this section, complete a piece of commentary that explains how infrastructure has developed over time in Addis Ababa and Ethiopia.
Explain the link between intermittent internet access in the country and political instability. This link will help.
Accelerated Growth - Thanks China!
Task 7 - Finally, to put all of this in context, read this September 2018 article from CNN. This wraps up a lot of what you have learnt and provides you with further information as to how Addis Ababa has developed so quickly. Clearly, this hasn't been done for free and as a gesture of goodwill. Highlight they key parts of report that detail major projects and those associated costs.
Now you are in a position to start writing up your response to the 10 mark question. Please refer to page 65-67 on the subject guide here for guidance on the mark scheme.
Urban deindustrialization - Focus on Detroit...
Whilst industry is booming in many MICs and LICs asa result of outsourcing and significant Direct Foreign Investment, there have been cases of severe urban deindustrialization in other parts of the world, notably in major HIC manufacturing cities such as Sheffield, UK (Steel), Glasgow, UK (ship building) and Detroit, USA (car manufacturing). For the purposes of this section of work, we will be focusing on the USA and the city of Detroit.
To complete this case study, you will need to use the following resources.
Resource 1 Causes and consequences- 22 minute Journeyman documentary & Abandoned Skyscrapers of Detroit (Independent)
To complete this case study, you will need to use the following resources.
Resource 1 Causes and consequences- 22 minute Journeyman documentary & Abandoned Skyscrapers of Detroit (Independent)
|
|
|
Resource 2 - Responses - Eminem (Promient Rapper from Detroit) & President Donald Trump.
|
|
|
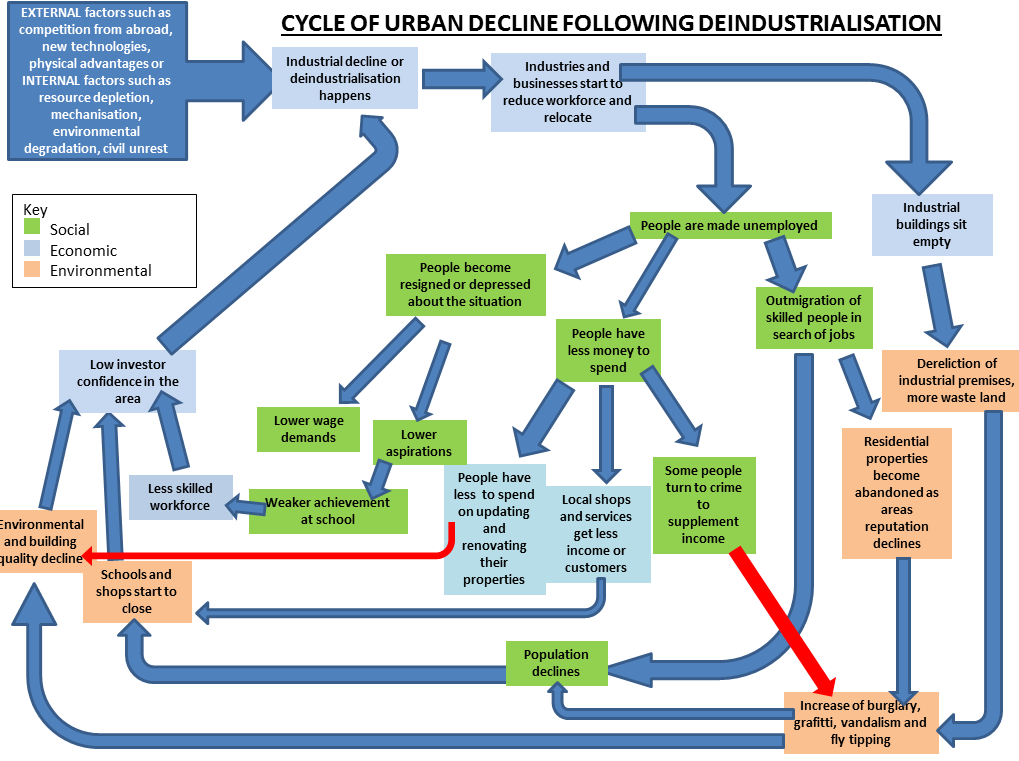
Resource 3 - Flow Diagram to show cycle of urban decline after deindustrialization.
Timed Essay - 25 Minutes
Examine the socio economic stresses resulting from deindustrialization in one or more urban areas (10)